- Visibility 42 Views
- Downloads 5 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.sajcrr.2022.017
-
CrossMark
- Citation
The first generation and second generation antipsychotic drugs and their pharmacology in treatment of schizophrenia
Introduction
Schizophrenia is complex, long-term mental illness illustrated by a many symptoms such as delusion, hallucination, speech disorders etc,. [1] “The word “Schizophrenia” comes from Greek word “Schizo” means “Split” & “Phrene” means “Mind”. In 1908, the term Schizophrenia was introduced by the Sweden psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler.[2] According to WHO, almost 20 million peoples worldwide suffer from a disease called schizophrenia [3] & WHO has declared schizophrenia to be one of the ten leading causes of developed countries in the world.[4] Antipsychotic means those drugs or medicines used to treat psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, schizoaffective conditions etc. In 1950, some new classes of medications come under the psychiatric practice such as antipsychotics. French pharmaceutical company Rhone-Poulenc synthesized chlorpromazine in 1950s, but not used in treatment of schizophrenia & In the US in 1960, the first clinical trial of chlorpromazine conducted with other antipsychotics. The two psychiatrics namely Jean Delay & Pierre Deniker used chlorpromazine on the patients who suffering from psychiatric disorder such as mania & schizophrenia.[5]
Schizophrenia is psychiatric disorders that are affect the thinking, behaves, emotions etc, of the patients. The symptoms of schizophrenia are commonly observed at the age of 16-30. The symptoms of schizophrenia are divided into three types: Positive, Negative & Cognitive symptoms.[6] Antipsychotics medications are principally used in treatment of schizophrenia & other psychotic disorders such as mental sickness, Bipolar disorder, etc. Antipsychotic medications are classified into two major classes Typical & Atypical it’s also called first & second generation drugs. [7] Antipsychotic drugs are taking around 7-14 days to reach their desire therapeutic effect. Antipsychotics unable to treat negative symptoms & able to treat / cure positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Atypical antipsychotics shows/ possess negative symptoms such as incapable to feel pleasure (Anhedonia), Alogia, Flattening, Apathy, Avolition etc,.[2]
Symptoms of Schizophrenia
The psychological symptoms of schizophrenia are divided into three main classes: Positive, Negative & Cognitive Symptoms. While Positive & Cognitive Symptoms are almost omnipresent in schizophrenia, Positive symptoms have unrelated with cognitive symptoms. However, this relationship appeared to be accompanied by negative symptoms. [8]
Positive symptoms
Positive symptoms are related with the hyperdopaminergic transmission occurring in the mesolimbic region of brain. Dopamine Receptor Antagonist drugs such as Chlorpromazine & Haloperidol are used to reduce the positive symptoms of schizophrenia.[9] It is associated with psychological behavior that is not widespread in an enthusiastic person. Suffering people may lose a touch of truth. Following some symptoms include such as delusions, hallucination, dysfunctional way of intellectual, agitated body movement, thought disorder & lack of speaking etc,.[6], [10]
Negative symptoms
A negative symptom indicates the abnormal normal mental function involving thoughts, behaviors & perceptions. [11] From these interruptions they can vary in general feelings and behaviors. The flat effect that the expression of emotions is reduced by facial expressions or tone of voice. Difficultly in initiating and sustaining activity and mutism (Speak Disorder).[10] In Negative Symptoms you might notice: Anhedonia, Alogia, Flattening, Apathy, Avolition etc. [11]
Cognitive symptoms
The cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia are belongs to thinking of persons. Although cognitive symptoms aren’t used to detect schizophrenia. [12] These symptoms can vary from person to person. [13] Victims may experience normal to serious changes in their intelligence or in any other aspect of thought. Symptoms may include difficulty concentrating; memory problem, lack of execution facilities, i.e. difficulty in understanding information & making decisions.[14] In it seen some symptoms such as Unable to Concentrate, Memory problems, Reduced Executive Function, Lack of Insight etc. [12]
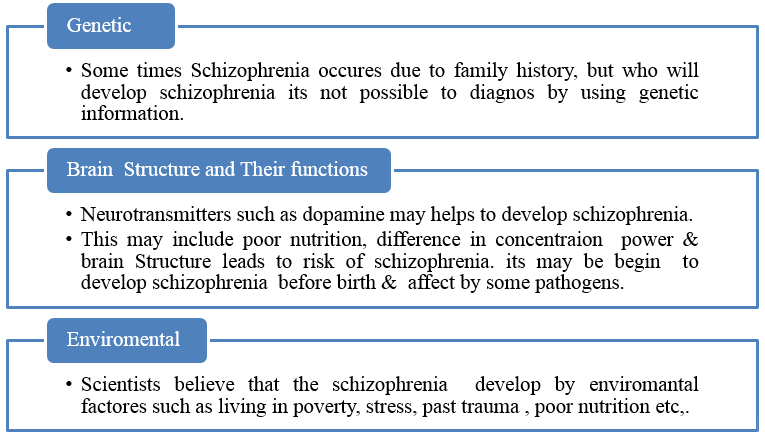
Causes
An exact cause of Schizophrenia is unknown. Researchers are continuously trying to find about the etiology of the disease. [15] But abnormal brain structure, enter-changes in neurotransmitter functioning, genetic & environmental factors causes schizophrenia. [16]
Risk Factor
Antipsychotic
Antipsychotic is a drugs which are used to treat symptoms of psychosis. They are also used to treat Schizophrenia, Depression, Bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorders & Anxiety. Antipsychotics drugs shows adverse effect. [16]
Classification of antipsychotic drugs
Antipsychotic drugs are classified into two subtypes such as Typical (First generation) & Atypical (Second generation). Typical medications have been used since the 1950s. It’s oldest or first type of antipsychotic drugs or medicines. Atypical medications have been used since the 1990s. It’s new or second type of antipsychotic class of drugs. [17] The use of antipsychotic drugs has the benefit of reducing the symptoms of psychosis and the risk of numerous side effects, including a difficult trade-off. Antipsychotic drugs are not therapeutic & do not eliminates long term thought disorders but they often negate the power of illusion, delusions & allow a person with schizophrenia to act in a caring situation. [18]

Antipsychotic medicine is a principle psychological strategy for the treatment of schizophrenia. These substances limit the effectiveness of treatment in individual patients & are associated with side effects. Taking antipsychotics is considered. While these drugs have no effect on negative symptoms. All of these drugs stop the action of postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptors. However, modern medicine has a wide spectrum of targeted Serotonin, nor epinephrine, Acetylcholine, Histamine & Glutamate. Clozapine, considered an Atypical antipsychotic, is associated with a variety of neuro-receptors (Dopamine, 5-HT serotonin & noradrenergic receptor) & and some acts as a multi-neuroreceptor antagonist. Clozapine is the most potent or highly effective antipsychotic drug & it’s does also reduce the risk of suicide of schizoaffective patients who tolerate to other antipsychotic drugs. [2]
Mechanism of Action
There are many drugs used to treat schizophrenia & they have different mechanism of action to create desired therapeutic effects. Mostly antipsychotics drugs help to treat Schizophrenia. [19]
1ST Generation
The first generation of antipsychotics follows inhibiting mechanism. They are highly effective when they block 72% of the D2 dopamine receptors in the brain. They also show antagonism action at the Noradrenergic, Cholinergic & Histaminergic receptors. It’s mainly used to treat positive symptoms such as hallucinations & delusions. [20], [19] In Typical antipsychotics show some adverse effect such extra-pyramidal side effects & anticholinergic adverse effect such as dry mouth, constipation etc. sedation, abnormal heart rates, sudden death, seizure threshold, hypotension, discoloration of skin, hydration, confusion, fever, acute renal failure etc, as well it’s have some contraindications like CNS depressant, cardiac abnormalities, history of allergy & seizure disorders, prostatic hypertrophy, dyskinesia, etc,.[20]
2ND Generation
The second generation of antipsychotics follows blocking mechanism. Its block the D2 dopamine receptors as well as serotonin receptors antagonist. 5-HT2A sub-type of the serotonin receptor is most commonly involved, thus may be associated with a reduce the risk of these adverse effect. In 2016, 12 Atypical Antipsychotics are approved by Food & Drug Administration (FDA). [20], [19] In Atypical antipsychotics show some side effects such as weight gain, metabolic syndrome development, dizziness, anxiety, sedation, thermo-sensitive, increased appetite, somnolence, hypotension, agitation, headache, restlessness, hyper salivation, etc,. and it have some contraindications like parkinsonism, narcoleptic, tardive dyskinesia, during pregnancy, glaucoma, liver disease, severe neutropenia, deficiency hexosaminidase etc,. [20]
Treatment
Antipsychotic drugs
Physician recommended a combination of psychotic drugs along with the psychotherapy.
Ayurvedic treatmeant
Brahmyadiyoga is an herbal preparation which is used in the treatment of Schizophrenia. Brahmyadiyoga developed by Central Council for Ayurvedic & Siddha, under Ministry of Health & Family Welfare of India. It includes Brahmi, Jatamansi, Sarpagandha, Vacha, Kusta, Tagar etc. For the treatment of schizophrenia, herbal combination of water-based extract of bramhi & Jatamansi are as effective as modern antipsychotics drugs. [21]
|
First-generation/ Typical antipsychotics |
|
||||||
|
Drugs |
Mechanism |
Adverse Effect |
Route |
Half-Life of Excretion |
Brand Name |
Metabolism |
Ref. |
|
Chlorpromazine |
Combined form of Chlorpromazine Antagonized Histamine (H1), Dopamine (D2) & Muscarinic (M1) receptors. |
Weight gain, sedation, acute movement disorder, parkinsonism, hypotension, dizziness, Akathisia, tardive dyskinesia etc. |
Oral, rectal, IM, IV |
30hr |
Largactil |
Hepatic |
|
|
Loxapine |
Antagonism of post synaptic Dopamine (D2) & serotonin (5-HT2) receptors |
Taste disorder (Dyspepsia), tardive dyskinesia, malignant syndrome, Depressogenic effect, Akathisia, etc. |
Oral, IM, Inhalation |
4-12hr |
Xylac, Adasuve |
Hepatic |
|
|
Prochlorperazine |
Blocking D2 receptor in brain, Histaminic, cholinergic & noradrenergic receptors. It’s Independent on dopamine antagonism. |
Dystonic reactions, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, Akathisia, Anorexia, loss of vision, sexual dysfunction, constipation, cardiac abnormalities, hypotension, dry mucosa, urinary retention, tardive dyskinesia, neuroleptoic malignant syndrome etc,. |
Oral, parenteral, IM & Rectal |
4-8hr |
Compazine, Stemetil |
Liver |
|
|
Thiothixene |
Antagonist of Dopamine (D1,D2,D3,D4), histamine, serotonin (5-HT1, 5-HT2), Cholinergic (M1,M2) & Alpha-Adrenergic receptor |
Muscle Stiffness, loss of vision, , Hand tremor, Dry Mouth, Coma, weakness, salivation, hypotension, tremors, neuroleptoic malignant syndrome etc,. |
Oral |
10-20hr |
Navane |
Hepatic |
|
|
Trifluoperazine |
Block dopamine D2 & D1 receptor in mesocortical & mesolimbic pathway. |
Akathisia, dystonia, parkinsonism, somnolence, xerostomia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, mydriasis, glaucoma etc. |
Oral, IM |
10-20hr |
Stelazine, Eskazinyl, Eskazine, Jatroneural |
Liver |
|
|
Thioridazine |
Block postsynaptic mesolimbic dopaminergic receptors in the brain. |
Shortness of breathing, tremor, swallowing trouble, hypotension, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, dizziness, restlessness, confusion, fever, sore throat, drowsiness, dry mouth & skin, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea etc., |
oral |
21-24hr |
Mellaril |
Hepatic |
|
|
Fluphenazine |
Antagonism of postsynaptic D2 receptors in mesolimbic, nigrostriatal & tuberoinfundibular neural pathway. |
Othrostatsis, Opisthotonos, dizziness, weight gain, tardive dyskinesia, Akathisia, Neuroleptic malignant syndrome, parkinsonian, hypotension, sedation, dry mouth & eyes, constipation, restlessness, Prolongation of QT, Sexual dysfunction, Galactorrhea, etc,. |
Oral, IM |
14-16hr |
Prolixin, Moditen |
Liver |
|
|
Haloperidol |
Block the dopaminergic receptors as well as noradrenergic, cholinergic & histaminergic blocking action. |
Breathing problems, headache, insomnia, anxious, irregular menstrual cycle, fever, dry skin & mouth, Acute Dystonia, Parkisonism, prolongation in QT, Hyperthermia, tardive dyskinesia etc. |
Oral, IM |
14.5-36.7hr |
Haldol |
Liver |
|
|
Pimozide |
Antagonism dopamine (D2) receptors. |
Akathisia, hyperhidrosis, nocturia, somnolence, speech disorder, sedation, dizziness, constipation etc. |
oral |
55hr |
Orap |
Hepatic |
|
Second-generation/ Atypical antipsychotics |
|||||||
|
Drugs |
Mechanism |
Adverse Effect |
Route |
Half Life of Excretion |
Brand Name |
Metabolism |
Ref. |
|
Aripiprazole |
Partial antagonist at D2 & 5HT1Areceptor & Antagonist at 5-HT2A receptor |
Akathisia, parkinsonian, acute Dystonic reactions, tardive dyskinesia, nausea, Weight gain, jaundice, etc. |
Oral, IM |
- |
Ability |
Liver |
|
|
Paliperidone |
Act Antagonist at dopamine, 5-HT2A , adrenergic, histaminic receptors |
Sedation, metabolic syndrome, weight gain, insomnia, somnolence, Akathisia, etc. |
Oral, IM |
42-77 days |
Xeolion, Invega |
Liver |
|
|
Risperidone |
Blocked D2 dopamine & (5-HT2A) serotonin receptors |
Sedation, metabolic syndrome, dystonia, Akathisia, parkinsonian, tremor, Gynecomastia, galactorrhea, hypertension, diabetes, tachypnea, tachycardia, dementia, etc. |
Oral |
20hr |
Risperdal |
liver |
|
|
Olanzapine |
May act by combination of dopamine & serotonin (5-HT2A) Antagonism |
Weight gain, decrease insulin sensitivity, metabolic dysfunction, Akathisia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, tardive dyskinesia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, extra pyramidal symptoms, glucosehomosasis, etc. |
Oral, IM |
21-54hr |
Zyprexa |
liver |
|
|
Clozapine |
Block dopamine & serotonin receptors |
Hyper salivation, myocarditis, agranulocytosis, constipation, dystonisa, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, seizures, etc. |
oral |
12hr |
Clozaril |
hepatic |
|
|
Asenapine |
Mechanism of action is unknown. It has been suggested that the combination of antagonist activity at D2 & 5-HT2A receptors |
Weight gain, Akathisia, parkinsonism, hypotension, dizziness, hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis, angioedema, wheezing, rashes, somnolence, oral hypothesis, cardiovascular diseases, |
Sublingual |
24hr |
Saphris |
hepatic |
|
|
Quetiapine |
Blocked Dopamine, histamine, Adrenergic, & serotonin nurotransmitters |
Sleepiness, constipation, weight gain, hypotension, seizures, prolonged erection, diabetes, tardive dyskinesia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, etc. |
oral |
6hr |
Seroquel |
liver |
|
|
Cariprazine |
Mechanism of action is unknown, but the action is mediated by combination of cariprazine of partial agonist at Dopamine (D2) & Serotonin (5-HT1A) as well as act as antagonist at serotonin (5-HT2A) receptors. |
Extra-pyramidal symptoms, weight gain, prolactin elevation, QTc prolongation, sedation, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, Anxiety, Insomnia, Akathisia, headache, Dyspepsia, vomiting, Somnolence, restlessness, etc. |
oral |
1 week |
Vraylar |
liver |
|
|
Iloperidone |
Dopamine D2 & 5-HT2A receptor antagonist & act as Neuroleptic Agent. |
Weight gain, Extrapyramidal symptoms, QTc prolongation, Orthostatic hypotension, prolactin elevation, Fatigue, nasal congestion, somnolence, tachycardia, dizziness, Tardive Dyskinesia, etc. |
Oral |
13 -18hr |
Fanapt |
liver |
|
|
Lurasidone |
Its show antagonistic activity by combination of dopamine (D2) & serotonin (5-HT2A). |
Akathisia, Somnolence, Parkinsonism, Dystonia, Nausea, Agitation, Anxiety, weight gain, etc. |
Oral |
18hr |
Latuda |
liver |
|
|
Ziprasidone |
Antagonized dopamine (D2) & serotonin in mesolimbic pathway & serotonin (5-HT2A) receptors in mesocortical pathway to reduce positive & negative symptoms respectively. |
Heart Palpitation, weight gain, depression, headache, anxiety, restlessness, Insomnia, drowsiness, Asthenia, Abdomen pain, hypertension, Rectal hemorrhage, dizziness, nausea, constipation, tremor, Rashes, Muscles pain, Stuffy nose, etc,. |
Oral, IM, |
7 - 10hr |
Geodon |
liver |
|
S.No. |
Herbal Plant |
Major Phytoconstituents |
|
1. |
Brahmi |
Asiaticoside & Bacoside |
|
2. |
Jatamansi |
Virolin & Jatamnsone |
|
3. |
Sarpagandha |
Reserpine & Ajmaline |
|
4. |
Vacha |
Asarone |
|
5. |
Kusta |
Costunolide & Palmitic acid |
|
6. |
Tagar |
Betulinic acid |
Conclusion
We concluded from this review article, schizophrenia is a complex psychiatric disorder that is belong to the disordering of brain improvement caused by environmental as well as some genetic factors. Most schizophrenia as well as psychotic disorders occurs due to abnormal brain structure & functioning. In this article we discuss about pharmacology of antipsychotics & Ayurvedic Treatment of psychosis. In that we observe delusion, hallucination, speech & behavior disorder like symptoms. In this we know about pharmacology of antipsychotics drugs but their exact causes of schizophrenia are unknown, I hope in future our researches are find exact causes of schizophrenia.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
References
- K R Patel, J Cherian, K Gohil, D Atkinson. Schizophrenia: overview and treatment options. P & T: a Peer-Reviewed J Formulary Manag 2014. [Google Scholar]
- H F Farah. Schizohrenia: An Overview. Asian J Pharm 2018. [Google Scholar]
- . Schizophrenia. World Health Organization. (2019, October 4). Retrieved from WHO. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia . [Google Scholar]
- B Kirkpatrick, B Miller, C Garcia-Rizo, E Fernandez-Egea. Schizophrenia: A Systemic Disorder. Clinical Schizophrenia & Realated Psychoses 2014. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- P Haddad, R Kirk, R Green. Chlopromazine, the first antipsychotic medication: history, controversy and legacy. (2016, October 31). Br Assoc Psychopharmacol 2016. [Google Scholar]
- H Kaur, R Kaur, V Rani, K Sharma, P Maurya. Antipsychotic Drugs. Advances in Neuropharmacology 2020. [Google Scholar]
- L John, JH Maccabe. Antipsychotic medication in schizophrenia: a review. Br Med Bull 2015. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Z U Khan, E Martin-Montanze, E C Muly. Schizophrenia: Causes and Treatments. Curr Pharm Des 2013. [Google Scholar]
- A G Nerkar, S B Bhise. Polypharmacological Drugs in Treatment of Schizophrenia. Curr Trends Pharm Pharml Chem 2020. [Google Scholar]
- AG Nerkar, SB Bhise. Schizophrenia: A Review. South Asian J Case Rep Rev 2019. [Google Scholar]
- . 11.Schizophrenia Symptoms: Positive and Negative Symptoms Explaind. (2020, december 13). . [Google Scholar]
- . How Schizophrenia is Diangnosid by Observing Symptoms. (2021, March 1). . [Google Scholar]
- P Collins. Psychological debriefing - are we doing more harm than good? Retrieved from blueline. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- K Volkan. Schizophrenia: Epidemiology, Causes, Neurobiology, Pathophysiology and Treatment. J Health Med Sci 2020. [Google Scholar]
- . National Institute of Mental Health. (2020, May). Schizophrenia. Retrieved from NIMH. . [Google Scholar]
- . Antipsychotics. (2021). Retrieved from Drugs.com. . [Google Scholar]
- . Antipsychotics - What you need to know. (n.d.). Retrieved from Rethink Mental Illness. . [Google Scholar]
- RA Harvey, MA Clark, R Finkel, JA Rey, K Whalen. Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology . 2011. [Google Scholar]
- . First versus second generation. (2021). Retrieved from NeuRA. . [Google Scholar]
- K Chokhawala, L Stevens. Antipsychotic Medications. (2021, October 2). 2021. [Google Scholar]
- A Chauhan, A Mittal, P K Arora. Atypical antipsychotics from scratch to the present. Int J Pharamaceutical Sci Res 2013. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- D Popovic, P Nuss, E Vieta. Revisiting loxapine: A systematic review. Ann General Psychiatry 2015. [Google Scholar]
- L Din, C V Preuss. . Prochlorperazine 2021. [Google Scholar]
- . Trifluoperazine. (n.d.). Retrieved Mar 17, 2022, from en.m.wikipedia.org. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- . Inxight Drugs. (2021, Oct). Retrieved from drugs.ncats.io. . [Google Scholar]
- S Siragusa, KG Bistas, A Saadabadi. Fluphenazine. (August 2021). 2021. [Google Scholar]
- S Rahman, R Marwaha. Haloperidol. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- . Pimozide Oral: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing. (n.d.). . [Google Scholar]
- N Gettu, A Saadabadi, A Saadabadi. . Aripiprazole. (2021, septeber 17) 2021. [Google Scholar]
- L Zhang, J Li, Y Zhao, Y Su, S Tianmei. Critical evalution of paliperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia in Chinese patients: asystematic literature review. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2016. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- SE Mcneil, JR Gibbons, M Cogburn. Risperidone. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- K Thomas, A Saadabadi. . Olanzapine 2021. [Google Scholar]
- J Rodrigues, M Bryan, . . Clozapine in the Treatment of Psychosis. Retrieved from physio-pedia.com . [Google Scholar]
- G Steven, J Potkin. Asenapine: A Clinical Overview. J Clin Psychiatry 2011. [Google Scholar]
- J S Maan, M Ershadi, I Khan, A Saadabadi. . Quetiapine 2021. [Google Scholar]
- I Laszlovszky, A Barabassy, G Nemeth. Cariprazine, A Broad-Spectrum Antipsychotic for the Treatment of Schizophrenia: Pharmacology, Efficacy, and Safety. Adv Ther 2021. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- L Citrome. Iloperidone: A clinical overview. J Clin Psychiatry . 2011;72 Suppl 1:19-23. 2011. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J M Kane. Lurasidone: A Clinical Overview. J Clin Psychiatry 2011. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- D Bouchette, K Fariba, R Marwaha. . Ziprasidone 2021. [Google Scholar]
- . 43.Atypical Antipsychotics. (2018, May). Retrieved from Drug.com. 2018. [Google Scholar]
