Introduction
Cataract accounts for roughly half of the world's blind people and is the most common preventable cause of blindness.1 According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a cataract is a clouding of the ocular lens that initially reduces vision but eventually progresses to blindness if left untreated.2 As a result, the person becomes more sensitive to light, has poor night vision, has double vision, and goes completely blind.3, 4 More than 50% of those who have cataracts have lost their vision.5
Cataract surgery is the only cataract treatment. The techniques for cataract surgery have also evolved from intracapsular cataract extraction technique to phacoemulsification.6, 7 All these methods require a thorough patient evaluation and workup for giving anaesthesia. With time there has been an evolution in anaesthesia for cataract surgery.8, 9
The delivery of anaesthesia has evolved from general anaesthesia to local anaesthetic, including retrobulbar, peribulbar, and sub-tenon, to topical anaesthetic. A good anaesthesia technique should guarantee the patient's comfort both during and after the operation. In general, the surgeon and patient must weigh the pros and cons of each anaesthetic type.10 The use of topical anaesthetic is clearly on the rise on a global scale.11 Today's anaesthesia for cataract surgery strives to make the operating room comfortable for both the patient and the surgeon and to promote a speedy return to normal function without posing additional hazards.
The most popular regional anaesthetic approach used widely to give anaesthesia for cataract extraction and intraocular lens implantation is the peribulbar block technique.12 When it is carried out by competent professionals, it is considered as a safe technique, especially when compared to retrobulbar block, which is linked to catastrophic and possibly fatal consequences. 13 Unless otherwise indicated, local anaesthetic is the preferred approach because it is simple, straightforward to perform, and causes no disruption to the patient's daily activities because it is a daycare procedure.14
The peribulbar technique is considered better than topical because it provides akinesia and is not completely dependent on patient cooperation. Whereas in topical technique the main disadvantage is it needs patient co-operation in addition to the surgeon's skills.15, 16, 17, 18 The most common local anaesthetic agent used for the peribulbar block is lignocaine hydrochloride 2% which is mixed with hyaluronidase to increase the dispersion of local anaesthetic around the orbit and for utilizing lesser volumes of local anaesthesia.19
During intraocular surgery, the intraocular pressure (IOP) rises significantly and may cause the vitreous to leak and increase the risk for oculocardiac reflex.20 An important element linked to an increase in IOP is the amount of local anaesthetic used in the peribulbar block. The volume of anaesthesia also depends on the size of the globe.21 Therefore, ensuring the volume of the block to be administered to get the desired effect is a crucial measure to prevent IOP rise.
This study aims to find out the relationship between the axial length of the eye and the minimal effective volume of the block to be administered to get the anaesthetic effect.
Materials and Methods
The study was a cross-sectional study conducted at a tertiary care hospital in Panipat. The study was done in the Department of Ophthalmology. The study was conducted for a period of 6 months from April 2023 to September 2023. The study includes 100 patients who were diagnosed with cataract and underwent cataract surgery after giving informed consent. The patients were divided into 2 groups based on the axial length of the eyeball. The first group includes patients with axial lengths between 21-23.99 mm and the second group includes patients with axial lengths of 24-26.99 mm.
Exclusion criteria
Patients who were allergic to lignocaine.
Patients with axial length <21 mm.
Patients with axial length >26.99 mm.
Patients with ocular infections.
Patients with systemic illnesses like hypertension, cardiac abnormalities, etc.
All patients who fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria were taken for the study. A thorough history was taken from all to rule out any systemic illness and allergic reaction to lignocaine. After the history, a complete workup was done which includes a slit lamp examination, intraocular pressure examination, and fundus examination. The grading of cataract was done, and patients with no other risk factors were planned for the surgery.
This was followed by blood investigations which included random blood sugar and viral markers. After this patient underwent keratometry and an A-scan for the calculation of lens power which was done by the same user to prevent bias. Keratometry was done using a manual keratometer which works on the principle that the anterior corneal surface behaves as a convex mirror and the size of the image falling on it changes with curvature.
A Scan (Biomedix Model- Echorule Pro Made in India) was done to get the axial length of the eyeball in millimeters. Axial length was calculated by touching the probe over the corneal tip and taking 7-8 readings and the average of all was taken as final reading. This was followed by the intraocular lens power calculation using the SRK-T formula for axial lengths of 21-24.5 mm and the Holladay-1 for axial lengths > 24.5 mm.
After this, a xylocaine sensitivity test (XST) was done by injecting 0.1-0.2 ml of undiluted lignocaine 2% subcutaneously into the forearm of the patient. The test was considered negative if there was no adverse reaction 30 minutes following the injection.
All this pre-operative workup was done for all patients and was followed by a peribulbar block before starting the surgery. Peribulbar block was made using 2% lignocaine with 1500 International Units of hyaluronidase. The patients in the first group were given 8 ml of block and in the in second group were given 6 ml of block. The subsequent doses of the block were given in those in which adequate response was not present.
The amount of the block given to each patient was noted and the data was recorded in Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet and the analysis was done using SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) software.
Results
In our study, we enrolled 100 patients who were divided into two groups 50 each based on the axial length of the eyeball. In all the patients, the XST was found to be negative and all other parameters are listed below.
Table 1
Shows the distribution of patients in both groups based on age group.
|
Age group |
Group 1 |
Group 2 |
|
41-50 |
2 |
3 |
|
51-60 |
16 |
7 |
|
61-70 |
17 |
19 |
|
71-80 |
11 |
17 |
|
81-90 |
4 |
4 |
|
Total |
50 |
50 |
As shown in the table the maximum number of patients in both groups lie in the age group of 61-70 years and the minimum number of patients were from the age group of 41-50 years.
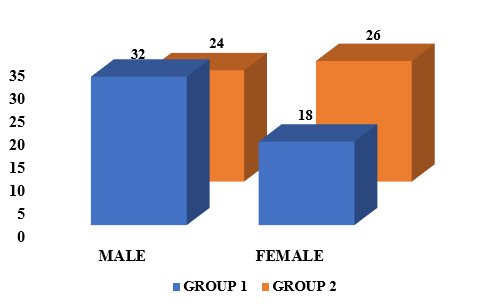
The graph shows that in group 1 the number of males (32) was more than that of females (18) but it was the opposite in group 2 with more females (26) in comparison to males (24).
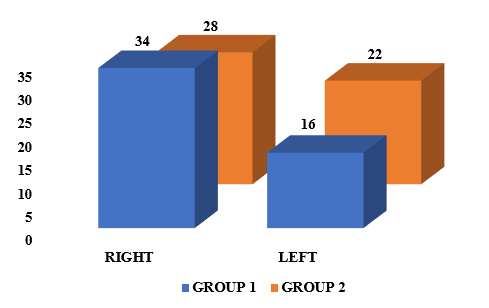
The graph shows that in both groups the number of patients being operated on the right eye was more in comparison to the left eye. The number of patients in group 1 who got operated on for the right eye was 34 and in group 2 it was 28 and the number of patients being operated on for the left eye was 16 in group 1 and 22 in group 2.
Table 2
Shows the distribution of patients in both groups according tothe grade of cataract.
|
Grade of cataract |
Group 1 |
Group 2 |
|
IMSC |
40 |
39 |
|
MSC |
4 |
3 |
|
HMSC |
6 |
8 |
The table shows that the maximum number of patients in both groups had immature senile cataract (IMSC). 40 patients from group 1 and 39 patients from group 2 had IMSC. It was also seen that 4 patients in group 1 and 3 patients in group 2 had mature senile cataract (MSC) and also 6 patients in group 1 and 8 patients in group 2 had hyper mature senile cataract (HMSC).
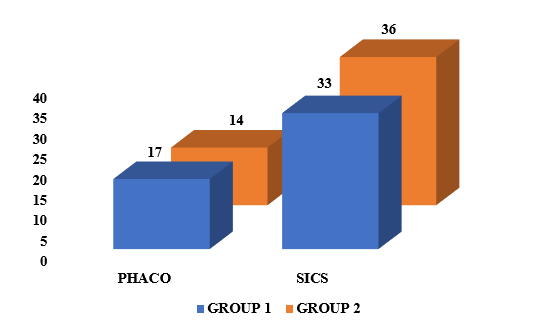
Graph 3 shows the distribution of patients according to the type of cataract surgery performed on them. It shows that in both groups the maximum number of patients (33 and 36) had undergone small incision cataract surgery (SICS). The number of patients who underwent phacoemulsification (PHACO) in group 1 was 17 and in group 2 it was 14.
Table 3
Shows the distribution according to the volume of peribulbar block given.
|
Volume |
Group 1 |
Group 2 |
|
6 |
0 |
39 |
|
7 |
0 |
8 |
|
8 |
34 |
3 |
|
9 |
7 |
0 |
|
10 |
8 |
0 |
|
12 |
1 |
0 |
|
Total |
50 |
50 |
The table shows that in group 1 the volume of peribulbar block given was higher than that in group 2. The maximum number of patients in group 1 (34) were given an 8 ml block and those in group 2 were given a 6 ml of block.
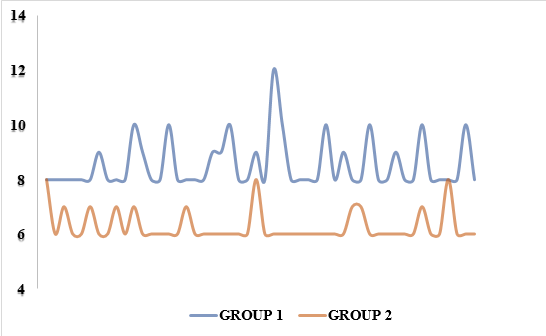
Scatter plot 1: Shows the distribution of patients in both groups based on the volume of the peribulbar group given.
The scatter plot shows that the volume of peribulbar block given in group 1 patients lies on a higher side than that in group 2 and the study had a significant p-value of 0.02.
Discussion
The eye is a human's primary organ of perception and vision. The orbit of the skull is where the eyeballs are located. Eyeballs are cystic formations that resemble almost spheres.22 In the emmetropic eye, the axial length (AL) is typically between 22 and 24 mm.23 The distance between the corneal surface and an interference peak that corresponds to the retinal pigment epithelium/Bruch's membrane is known as AL.24, 25
Axial length is measured using an A-scan. It creates a picture and measurements of the eye by projecting 10 mHz soundwaves and recording the echoes that return from ocular structures. A-scan ultrasonography, as the name suggests, necessitates applanation because the device uses a transducer that necessitates direct contact with the eye. The negative effect of this approach is patient discomfort. The direct contact of the transducer with the cornea often results in corneal compression, which reduces corneal thickness or anterior chamber depth, which artificially lowers axial length readings.26, 27 A-scan has a repeatability of between 0.2 and 0.3 millimeters.28, 29
There are currently no documented clinically meaningful predictors of the necessary dosage of a local anaesthetic to deliver adequate akinesia and anaesthesia. In clinical practice, volumes between 6 and 10 mL are typical. Therefore, getting the ideal injected volume is crucial since both inadequate and excessive quantities can harm. Insufficient volumes can result in inadequate blocks. Elevated quantities might elevate IOP dangerously. On the other side, oculocardiac reflex, vitreous prolapse, and acute ischemic optic neuropathy are associated with IOP elevation. 21, 30
In our study, we found that in group 1 the volume of peribulbar block given was higher than that in group 2. The maximum number of patients in group 1 (34) were given an 8 ml block and those in group 2 were given a 6 ml of block. This is supported by the fact that the more the axial length the lesser the intraorbital space to accommodate the injected volume of the block.
Conclusion
In our study, we found that axial length has a negative correlation with the volume of the peribulbar block. The more the axial length of the eye the less the amount of peribulbar block required for an anaesthetic effect. This is supported by the fact that the more the axial length the lesser the intraorbital space to accommodate the injected volume of the block.